Showing posts with label inverter. Show all posts
Showing posts with label inverter. Show all posts
Tuesday, September 10, 2013
12V to 220V 100W Transistor Inverter Circuit Diagram
12V to 220V 100W Transistor Inverter Circuit Diagram

12V to 220V 100W transistor based power inverter.
Friday, August 2, 2013
Simple 12 Vdc 120 Vac Inverter Circiut
An Inverter is a device that converts 12 volts d.c to 120 volts a.c. , which is what we use in our homes. This project will handle about 300 watts, which is perfect for lights, small T.V.s and radio equipment.
This Inverter takes 12 volt d.c and steps it up to 120 volt a.c. The wattage depends on which transistors you use for Q1 and Q2, as well as the "Amp Rating" of the transformer you use for T1. This inverter can be constructed to supply anywhere from 1 to 1000 (1 KW) watts. If Q1, Q2 are 2N3055 NPN Transistors and T1 is a 15 A transformer, then the inverter will supply about 300 watts. Larger transformers and more powerful transistors can be substituted for T1, Q1 and Q2 for more power. Note: Dont try to run inductive loads (motors...) off this inverter.
This Inverter takes 12 volt d.c and steps it up to 120 volt a.c. The wattage depends on which transistors you use for Q1 and Q2, as well as the "Amp Rating" of the transformer you use for T1. This inverter can be constructed to supply anywhere from 1 to 1000 (1 KW) watts. If Q1, Q2 are 2N3055 NPN Transistors and T1 is a 15 A transformer, then the inverter will supply about 300 watts. Larger transformers and more powerful transistors can be substituted for T1, Q1 and Q2 for more power. Note: Dont try to run inductive loads (motors...) off this inverter.
12 Vdc - 120 Vac Inverter Circuit Diagram
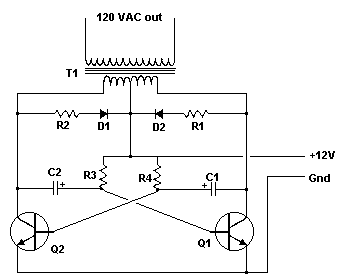
Parts:
C1, C2 68 uf, 25 V Tantalum Capacitor
R1, R2 10 Ohm, 5 Watt Resistor
R3, R4 180 Ohm, 1 Watt Resistor
D1, D2 HEP 154 Silicon Diode
Q1, Q2 2N3055 NPN Transistor (see "Notes")
T1 24V, Center Tapped Transformer
Misc. Wire, Case, Receptacle (for output)
Fuses, Heatsinks, etc.
Caution: This circuit can cause serious injury or death. Keep away from children. Source Link
C1, C2 68 uf, 25 V Tantalum Capacitor
R1, R2 10 Ohm, 5 Watt Resistor
R3, R4 180 Ohm, 1 Watt Resistor
D1, D2 HEP 154 Silicon Diode
Q1, Q2 2N3055 NPN Transistor (see "Notes")
T1 24V, Center Tapped Transformer
Misc. Wire, Case, Receptacle (for output)
Fuses, Heatsinks, etc.
Caution: This circuit can cause serious injury or death. Keep away from children. Source Link
Wednesday, July 10, 2013
Build a 500W Low Cost 12V to 220V Inverter
Attention: This Circuit is using high voltage that is lethal. Please take appropriate precautions
Using this circuit you can convert the 12V dc in to the 220V Ac. In this circuit 4047 is use to generate the square wave of 50hz and amplify the current and then amplify the voltage by using the step transformer.
How to calculate transformer rating
The basic formula is P=VI and between input output of the transformer we have Power input = Power output
Using this circuit you can convert the 12V dc in to the 220V Ac. In this circuit 4047 is use to generate the square wave of 50hz and amplify the current and then amplify the voltage by using the step transformer.
How to calculate transformer rating
The basic formula is P=VI and between input output of the transformer we have Power input = Power output
For example if we want a 220W output at 220V then we need 1A at the output. Then at the input we must have at least 18.3V at 12V because: 12V*18.3 = 220v*1
So you have to wind the step up transformer 12v to 220v but input winding must be capable to bear 20A.

Monday, July 8, 2013
230 Volt AC To Inverter Switching Circuit Diagram

Before three weeks i am introduced inverter circuit diagram but the circuit not included ac to inverter switching part so today i introducing a 230 Volt Ac to inverer switching circuit diagram .
Circuit showing a inverter switching . Here i have used bc 558 ,BC 548 and a relay for making this circuit . 230 volt connected to the base of the transistor Q1.When the power is ON positive volt coming to the base of the transistor so the relay circuit is open and load working in 230 V AC .When the power is OFF ground voltage coming to the base of the transistor so the Base of the Q2 is positive there for the relay circuit closed and load working in inverter input .Part list and applications are showing below.
Part List
| Component No: | Value | Usage |
| R1 | 100KΩ | Emitter Load |
| R2 | 10K Ω | Base Biasing |
| R3 | 180KΩ | Current Limiting |
| Q1 | BC558 | Switching |
| Q2 | BC548 | Switching |
| D1 | IN4007 | Relay Balancing |
| RL1 | 12 V | Inverter Switching |
Applications
* Inverter Switching
* AC Switching
Thursday, March 28, 2013
Discrete Voltage Inverter
The circuit in the diagram enables a negative voltage to be derived without the use of integrated circuits. Instead, it uses five n-p-n transistors that are driven by a 1 kHz (approx) TTL clock. When the clock input is high, transistors T1 and T2 link capacitor C1 to the supply voltage, UIN, which typically is 5 V. During this process, transistor T5 conducts so that T3 and T4 are off. When the clock input is low, T5 is cut off, whereupon transistors T3 and T4 are switched on via pull-up resistor R6 and either R4 or R5.
 This results in the charge on C1 being shared between this capacitor and C2 Since the +ve terminal of C2 is at ground potential, its –ve terminal must become negative w.r.t. earth. The high level at the clock input must be of the same order as the positive input voltage, UIN, otherwise T1 cannot be switched on. The clock frequency should be around 1 kHz to ensure a duty cycle ratio of 1:1. Altering the ratio results in a different level of negative output voltage, but this is always smaller than that with a ratio of 1:1.
This results in the charge on C1 being shared between this capacitor and C2 Since the +ve terminal of C2 is at ground potential, its –ve terminal must become negative w.r.t. earth. The high level at the clock input must be of the same order as the positive input voltage, UIN, otherwise T1 cannot be switched on. The clock frequency should be around 1 kHz to ensure a duty cycle ratio of 1:1. Altering the ratio results in a different level of negative output voltage, but this is always smaller than that with a ratio of 1:1.
Read the rest entry[...]
 This results in the charge on C1 being shared between this capacitor and C2 Since the +ve terminal of C2 is at ground potential, its –ve terminal must become negative w.r.t. earth. The high level at the clock input must be of the same order as the positive input voltage, UIN, otherwise T1 cannot be switched on. The clock frequency should be around 1 kHz to ensure a duty cycle ratio of 1:1. Altering the ratio results in a different level of negative output voltage, but this is always smaller than that with a ratio of 1:1.
This results in the charge on C1 being shared between this capacitor and C2 Since the +ve terminal of C2 is at ground potential, its –ve terminal must become negative w.r.t. earth. The high level at the clock input must be of the same order as the positive input voltage, UIN, otherwise T1 cannot be switched on. The clock frequency should be around 1 kHz to ensure a duty cycle ratio of 1:1. Altering the ratio results in a different level of negative output voltage, but this is always smaller than that with a ratio of 1:1.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)