Friday, December 27, 2013
Long Range FM Transmitter

- L1 - 4 turns of 20 SWG wire close wound over 8mm diameter plastic former.
- L2 - 2 turns of 24 SWG wire near top end of L1.(Note: No core (i.e. air core) is used for the above coils)
- L3 - 7 turns of 24 SWG wire close wound with 4mm diameter air core.
- L4 - 7 turns of 24 SWG wire-wound on a ferrite bead (as choke)
Thursday, December 26, 2013
Simple Gated Alarm
Circuit diagram :

IC1.A is a slow oscillator which is enabled when reset pin 4 is taken High, and inhibited when it is taken Low. Out-put pin 5 of IC1.A pulses audio oscillator IC1.B, which is similarly enabled when reset pin 10 is taken High, and inhibited when it is taken Low.
In order to simplify oscillator IC1.B, piezo sounder X1 doubles as both timing capacitor and sounder. This is possible because a passive piezo sounder typically has a capacitance of a few tens of nanofarads, although this may vary greatly. As the capacitor-sounder charges and discharges, so a tone is emitted. The value of resistor R2 needs to be selected so as to find the resonant frequency of the piezo sounder, and with this its maximum volume. The circuit will operate off any sup-ply voltage between 2 V and 18 V. A satisfactory output will be obtained at relatively high supply voltages, but do not exceed 18 V.
Wednesday, December 25, 2013
The mutual inspection of cell phone jammer should also be performed
In addition, the rural market is a new market segment, a large number of competitors have not yet entered the competition is not intense, very favorable for Amagatarai phone. Monopolistic tendencies of foreign brands on the channel, so for phones Amagatarai, the key point is to find a breakthrough, in order to build a massive distribution network, the best way is the coexistence of a variety of sales channels. Day language mobile phone retailers, specialty retail, home appliance chain stores, specialized chains and integrated supermarkets, such as shopping malls, supermarkets, etc. should be selected. Different buying habits of consumers, to choose a different retailer, to expand the sales network, to ensure that each class of customers with access to day language phone products. Workshop management of cell phone jammer plays an important role in manufacturing cell phone jammer .cell phone jammer can create enough interference to jam all cell phone signals
To meet the economic characteristics of the contemporary Amagatarai phone channels, the channel length should not be too long, If it is too long, then one for each level distributors to charge some of the profits to the final price of natural variability, is not conducive to the promotion of sales. Flat channel is more conducive to day language is more direct and fast communication with consumers, receive timely feedback information, accurate information on market trends. But the need for a clear channel flat in real terms is the abatement of long and useless links and improve operational efficiency. Constructed between the distributors and consumers of Amagatarai into a complete, organic, and efficient network system. If the worker has any suggestion about workshop management of cell phone jammer , heshe can write a letter to the director.
If the flattening channels of day language to be unrestricted, would like the cost investment in the channel is larger, to centralize power in the distributors, and makes Amagatarai manufacturers in a passive situation. The present tendency of the mobile phone market, the mobile phone hypermarkets position in the market has become increasingly prominent, not only as the Dixon type of specialized cell phone store, and supermarket chains like Gome, Suning, Five Star appliances have also joined. It is due to join supermarkets in the distribution process, the language needs to put in more effort and resources in promoting store sales above. Amagatarai phone should make full use of the advantage of localization and mobile connectivity and other operators to launch a customized mobile phone, meet the diverse needs of consumers. cell phone jammer can create enough interference to jam all cell phone signals.
Tuesday, December 24, 2013
Electric Guitar Preamplifier

Electric Guitar Preamplifier Circuit diagram:

Monday, December 23, 2013
Please inquire any time any nonconforming part of cell phone jammer is found
Wang Lei Leis remarks revealed the "wireless value-added services must rely on win-win" of the mystery. As Chinas leading Internet brands, TOM Onlines focus on the young and trendy demographic, including wireless Internet services and online advertising services. Business scope covers, including SMS, MMS, WAP, wireless interactive services (IVR), content channels, search, classified information, free and paid email services and online games fields. In 2004, TOM Online and the worlds leading instant messaging company Skype co-released multi-TOM-Skype calls for free software. Several cell phone jammer shielding positions will be installed in the whole prison zone.Long currently offers e 230 major cities in China nearly 2,800 hotels and more than 40 000 overseas hotel discount reservation service, domestic more than 50 major business and tourist city out, delivery ticket services, and vacation, group travel, car rental and other travel services. October 2004 e dragon in the U.S. NASDAQ market, the worlds largest online travel company Expedia has a 52% stake in e dragon. Currently, e dragon has become a core part of Expedia Asia, and its in the UK, Canada, Germany, France and other countries, companies, working together to provide consumers with fresh and satisfying travel experience. Today, e dragon work closely with Expedia.
The word is actually simple to do it simple, for the different applications it has different meanings: For an application, you may need a simple installation process, a simple mode of operation; for a website, search engines, users may need to directly address the needs of and not to click time and time again, page after page of the browser. Integration. "Lazy" is the driving force of social development, who can make the user more and more "lazy" will succeed. Integrate it means the user needs to organize information and core functions, for maneuver, showing a lack of cell cell phones, this is even more important. This can be roughly divided into two categories: one is the aggregation of information, but not the accumulation of clutter, but also by integrating the needs of users present, but in fact involves a lot of complicated technology. cell phone jammer intelligent management system is the branch of the wireless information detecting and shielding system.
Another is the integration of functions, which is sought to provide one-stop service - to open the software, looking around the restaurant, find a favorite restaurant scheduled to direct dial the cell phone to receive coupons, easy to use map navigation to cell phones. Shopsavvys success is due to this. Accurate. Accurate integration of the above-mentioned fact, and is one of the integration is the basis of accurate analysis of user needs. Better precision on the one hand to make the user experience, easy access to needed information and applications; the other hand, let advertisers excited, precision will help advertisers target users even more easily accessible to facilitate transactions. LBS, SNS, user behavior analysis and other technologies, will in the future mobile Internet is widely used, a clear picture from all sides of each user, to achieve accurate.
Saturday, December 21, 2013
5V Regulated Power Supply Circuit Diagram
Circuit diagram of 5V Regulated Power Supply
 |
| Fig-1: 5V regulated power supply schematic |
Pin Diagram of IC 7805
 |
| Fig2:Pin Diagram of IC 7805 |
Friday, December 20, 2013
Two Transistor AM Transmitter
Circuit diagram:

Simple AM Transmitter Circuit Diagram
To tune it to a particular frequency, reduce one or both of the 220pF capacitors to raise the frequency or add capacitance in parallel to lower the frequency. Q1 is biased with a 1MO resistor to give a high input impedance and this allows the use of a crystal ear piece as a low cost microphone.
Thursday, December 19, 2013
Song Music generator circuit using ic UM66
Circuit Diagram of Music generator using ic UM66:
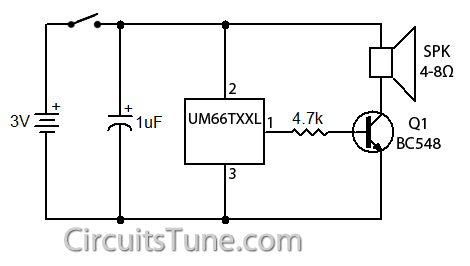 |
| Fig: Circuit Diagram of Song-Music generator using IC-UM66 |
UM66TXX series IC generate different songs-music, the song-music depends on the model of UM66TXX series IC’s. The song-music are listed below with model number.
UM66TXX Songs List:
UM66T01 = Jingle Bells + Santa Claus is coming to town + Wish you a Merry Xmas
UM66T02 = Jingle Bells
UM66T04 = Jingle Bells + Rudolph, the red-nosed reindeer + Joy the world
UM66T05 = Home sweet home
UM66T06 = Let me call you sweetheart
UM66T08 = Happy birthday to you
UM66T09 = Wedding march
UM66T11 = Love me tender, Love me true
UM66T13 = Easter parade
UM66T19 = For Elise
UM66T32 = Waltz
UM66T33 = Mary had a little lamb
UM66T34 = The train is running fast
UM66T68 = Its small world
Wednesday, December 18, 2013
Easy Loudspeaker Circuit For Telephone

- Power rectifier and filter section
This section is made of a simple bridge rectifier and a indicating power LED. - Voltage regulator section
This section is made upon transistor Sl100, which is a general purpose NPN transistor in metal package. That is used to regulate voltage at a level of 9+0.6=9.6V by a 9V zener diode. - Speaker output section
This section contains a high impedance speaker and two BC548 NPN transistor to amplify the signal from line, the input of the 548 transistor pair is fed with a linear or pot control of 10K for volume adjust. - Microphone input section
This section contains a condenser microphone (tablet) and two BC548 NPN transistor to amplify the signal from mic, the output of the 548 transistor pair is fed with a linear or pot control of 10K for volume adjust to the line.
Tuesday, December 17, 2013
Build a Power supply Protection Circuit Diagram
Power supply Protection Circuit Diagram

The trip voltage is set to 5.7 V to protect the equipment in the event of a regulator fault. The 330 ohm resistor and the 500 ohm potentiometer form a potential divider which samples the output voltage as set by adjustment of the potentiometer. The SCR is selected to carry at least twice the fuse rating. The full supply voltage is connected to the input of the regulator.
The 2N2906 is held bias off by the 10 k resistor and the SCR so that the LED is held off. If the output voltage rises above a set trip value then the SCR will conduct, the fuse will blow, and the 2N3906 will be supplied with base current via the 10 k resistor, and the LED will light up.
Wednesday, October 9, 2013
Hi Fi Headphone Amplifier
This design for a headphone amplifier arose after the purchase of commercial equipment with separate pre and power amplifiers without a headphone output.
It is based on designs for a headphone amplifier by John Linsley-Hood, and an active volume control, using a linear pot, by Doug Self (the "pot" circuit was originally designed by P.J. Baxandall), both published in Electronics and Wireless World in recent years.
Its advantages are ...
- is independent of the absolute value of the pot
- has excellent channel tracking
- the O/P noise reduces with gain reduction.
Description
The intention is to permanently insert the headphone amp between pre and power amps, although it can be used as a stand-alone item. The input relay is operated by auxiliary contacts on the headphone sockets through a transistor driver (with a small delay) so as to mute the power amp input when listening on headphones.
The relay contact arrangement enabling it (the headphone amp) to be left switched off when normally not in use. The relay is a high quality, sealed, gold plated contact, TQ signal switching type, reputedly with a very long life expectancy.
The gain control being used to pre-set the gain so that the pre-amps gain control is normally used for setting the listening level.
 Figure 1 - The Headphone Amp Circuit
Figure 1 - The Headphone Amp Circuit
One channel only is shown, so two units are required for stereo. The gain control pot must be a dual-gang linear type, as the circuit configuration provides the logarithmic law required. This is similar to the circuit shown in Project 01 (except that this version provides a useful reduction of noise). A value of 47k or 100k should be fine in this circuit. Diodes should be 1N4148.
The first stage is a conventional series feedback circuit using the ubiquitous NE5534, the gain being set by the feedback AOT (adjust on test) resistor to suit individual needs, this stage provides the necessary low impedance output for the variable gain stage. The resistor/ capacitor networks around the input stage may seem a little extravagant, but are necessary to reduce any possible RF pickup especially the 470 pF between the two IC + and - inputs.
The complete second stage consists of a zero gain follower, an inverting gain stage and the output emitter followers, volume control gain being set around these three stages. The x10 gain of the inverting stage gives the closest approach to a logarithmic law, stability being ensured by the 27pf capacitor in this stages feedback. The output complementary pair runs in Class-A at about 80 mA and should be mounted on a small heatsink.
Dissipation is about 1.8 Watts for each device, and they must be isolated from the heatsink with mica washers and mounting bushes to prevent short-circuiting the power supply (the collectors are connected to the case). Make sure that heat-conducting paste is used, or use sil-pads for mounting - these require no thermal compound and are very convenient for low power operation.
 Figure 2 - Alternative Relay Driver, and Component Pinouts
Figure 2 - Alternative Relay Driver, and Component Pinouts
The OPA2604 was chosen because its high, FET based, input impedance provides better DC conditions for setting the O/P at 0V DC than the NE5532 alternative, its low output impedance has no problems in driving difficult loads, but it is still relatively cheap.
The power supply is a fairly conventional split variety, the regulated O/Ps feeding the ICs - note the decoupling arrangements - and the 22V pre-regulated supply feeding the O/P transistors, the relay supply being rectified and regulated separately for the necessary isolation, separate signal and supply star earthing being essential
The output jack sockets, with independent changeover contacts, are obtainable from Maplin Electronics and have proved extremely reliable over many years of regular use. If these are not obtainable a circuit is included for use with conventional break contact jack sockets.The LED series resistors will need to supply a current of about 7.5mA, so 2.2k should be used. Diodes for the supply should be 1N4004 or equivalent.
If desired, the 12V regulator may be dispensed with, and suitable value resistors placed in series with each relay coil to retain the correct operating voltage. It is the constructors responsibility to determine the value of these, as the relay current cannot be predicted as there are so many different types available. Use of 15V relays is also possible, if available.
If this arrangement is used, a slight amount of noise may be introduced as the relay operates, because of the sudden application (or removal) of the additional load. It is not expected that this would be a problem in use.
My thanks to Richard for submitting this circuit - it is sure to provide a very high sound quality, and is not overly complex. The active gain control (originally designed by Peter Baxandall) is very effective.
As always, resistors should be 1% metal film types for all signal paths. Their use in the power supply and relay circuits is not necessary, but will not do any harm, either.
Source:www.sound.westhost.com
Tuesday, October 8, 2013
AUDIO SCHEMATIC AND ROUTING ELECTRONIC DIAGRAM
It shows the connection and wiring between each parts and component of audio system of the vehicle such as the alternator, ignition switch, antenna meter, tail, audio, front speaker, rear speaker, tweeter speaker, and many more.
Monday, October 7, 2013
Crowbar Speaker Protection
Crowbar circuits are so-called because their operation is the equivalent of dropping a crowbar (large steel digging implement) across the terminals. It is only ever used as a last resort, and can only be used where the attached circuit is properly fused or incorporates other protective measures.
A crowbar circuit is potentially destructive - if the circuitry only has a minor fault, it will be a major fault by the time a crowbar has done its job. It is not uncommon for the crowbar circuit to be destroyed as well - the purpose is to protect the device(s) attached to the circuit - in this case, a loudspeaker.
Description
Theres really nothing to it. A resistor / capacitor circuit isolates the trigger circuit from normal AC signals. Should there be enough DC to activate the DIAC trigger, the cap is discharged into the gate of the TRIAC, which instantly turns on ... hard. A TRIAC has two basic states, on and off. The in-between state exists, but is so fast that it can be ignored for all intents and purposes.
 Figure 1 - Crowbar Speaker Protector
Figure 1 - Crowbar Speaker Protector
The BR100 DIAC (or the equivalent DB3 from ST Microelectronics) is rated for a breakdown voltage of between 28 and 36V - these are not precision devices. Needless to say, using the circuit with supply voltages less than around 40V is not recommended, as you will have a false sense of security. The supply voltage must be higher than the breakdown voltage of the DIAC, or it cannot conduct. Zeners cannot be used as a substitute for lower voltages - a DIAC has a negative impedance characteristic, so when it conducts, it will dump almost the full charge in C1 into the gate of the TRIAC. This is essential to make sure the TRIAC is switched into conduction.
The TRIAC is a common type, and may be substituted if you know the specifications. Its rated at 12A, but the peak current (non-repetitive) is 95A, and it only needs to sustain that until the fuse (or an output transistor) blows. A heatsink is preferred, but there is a good chance that the TRIAC will blow up if it has to protect your speakers, so it may not matter too much. The 0.47 ohm resistor is simply to ensure that the short circuit isnt absolute. This will limit the current a little, and increases the chance that the TRIAC will survive (albeit marginally). Feel free to use a BT139 if it makes you feel better - these are rated at 16A continuous, and 140A non-repetitive peak current.
The peak short circuit current will typically be about 90A for a ±60V supply, allowing ~0.2 ohms for wiring resistance and the intrinsic internal resistance of the TRIAC, plus the equivalent series resistance of the filter capacitors. Thats a seriously high current, and it will do an injury to anything thats part of the discharge path. Such high currents are not advised for filter caps either, but being non-repetitive they will almost certainly survive.
Construction & Use
Apart from the obvious requirement that you dont make any mistakes, construction is not critical. Wiring needs to be of a reasonable gauge, and should be tied down with cable ties or similar. C1 must be polyester. While a non-polarised electrolytic would seem to be acceptable, the circuit will operate if the capacitor should dry out over the years. This means it will lose capacitance, and at some point, the crowbar may operate on normal programme material. This would not be good, as it will blow up your amplifier!
Make sure that all connections are secure and well soldered. Remember that this is the last chance for your speakers, so it needs to be able to remain inactive for years and years - hopefully it will never happen. The circuit doesnt have to be mounted in the amplifier chassis - it can be installed in your speaker cabinet. Nothing gets hot unless it operates, at which point no-one really cares - it just has to save the speakers from destruction once to have been worthwhile.
Remember that the crowbar circuit absolutely must never be allowed to operate with any normal signal. A perfectly good amplifier that triggers the circuit because of a high-level bass signal (for example) will very likely be seriously damaged if the crowbar activates. To verify that no signal can trigger it, you may want to (temporarily) use a small lamp in place of R2, and drive the amp to maximum power with bass-heavy material.
A speaker does not need to be connected. If the lamp flashes, your amp would have been damaged. If this occurs, you may want to increase the value of C1. Note that bipolar electrolytics should never be used for C1, because they can dry out and lose capacitance as they age. This could cause the circuit to false-trigger.
Source :www.extremecircuits.net
Sunday, October 6, 2013
METAL DETECTOR USING BEAT FREQUENCY OSCILLATOR ELECTRONIC DIAGRAM
The NAND gates use CMOS 4011 chip, a low power component that is suitable for this battery-operated circuit. You can see that this chip is supplied by a 5V voltage coming from an LM7805L regulator. You might wonder what the purpose of this regulation is, since the power supply come from a 9V battery and the CMOS gates can handle the voltage of 3-15 Volt. The main purpose of the regulator is to keep a constant voltage source for the reference oscillator frequency stability, since the frequency is affected by the power supply voltage variation as the battery voltage drops in the long time of usage.
This circuit uses parts as follows :
- U1: CD4011
- U2: LM389
- U3: 78L05
- R1: 2.2k 5%
- P2: 4.7k lin.
- R3: 330k 5%
- R4: 270k 5%
- R5: 1k 5%
- C1: 390pF (NPO)
- C2,C3,C4: 10nF
- C5: 10uF 16v electrolytic
- C6,C8: 220 uF 16v electrolytic
- C7: 100uf 16v electrolytic
- C9: 100nF ceramic
- P1: 4.7k log
- L1: 22cm in diameter with 14 turns AWG 26
- K1: SPDT toggle switch
- J1= Headphone jack 1/4 or 1/8 inch
- Other parts: 9v battery connector, speaker or headphones
Saturday, October 5, 2013
Baud Rate Generator
In this article, an RC oscillator is used as a baud rate generator. If you can calibrate the frequency of such a circuit sufficiently accurately (within a few percent) using a frequency meter, it will work very well. However, it may well drift a bit after some time, and then…. Consequently, here we present a small crystal-controlled oscillator. If you start with a crystal frequency of 2.45765 MHz and divide it by multiples of 2, you can very nicely obtain the well-known baud rates of 9600, 4800, 2400, 600, 300, 150 and 75. If you look closely at this series, you will see that 1200 baud is missing, since divider in the 4060 has no Q10 output!
If you do not need 1200 baud, this is not a problem. However, seeing that 1200 baud is used in practice more often than 600 baud, we have put a divide-by-two stage in the circuit after the 4060, in the form of a 74HC74 flip-flop. This yields a similar series of baud rates, in which 600 baud is missing. The trimmer is for the calibration purists; a 33 pF capacitor will usually provide sufficient accuracy. The current consumption of this circuit is very low (around 1mA), thanks to the use of CMOS components.
Friday, October 4, 2013
High Side Current Measurements
This current can be used directly, or it can be converted into a voltage by means of a load resistor RL. In the latter case, the ‘floating’ measurement voltage across the shunt is converted into a voltage with respect to earth, which is easy to use. The value of RL determines the gain. A value of 5 kΩ gives 1×, 10 kΩ gives 2×, 15 kΩ gives 3× and so on. It all works as follows. Just like any opamp, this IC tries to maintain the same potential on its internal plus and minus inputs. The minus input is connected to the left-hand end of the shunt resistor via a 5-kΩ resistor.
 When a current flows through the shunt, this voltage is thus lower than the voltage on the plus side. However, the voltage on the plus input can be reduced by allowing a small supplementary current to flow through T1. The IC thus allows T1 to conduct just enough to achieve the necessary lower voltage on the plus input. The current that is needed for this is equal to Vshunt / 5 kΩ. This transistor current leaves the IC via the output to which RL is connected. If the value of RL is 5 kΩ, the resulting voltage is exactly the same as Vshunt. The IC is available in two versions.
When a current flows through the shunt, this voltage is thus lower than the voltage on the plus side. However, the voltage on the plus input can be reduced by allowing a small supplementary current to flow through T1. The IC thus allows T1 to conduct just enough to achieve the necessary lower voltage on the plus input. The current that is needed for this is equal to Vshunt / 5 kΩ. This transistor current leaves the IC via the output to which RL is connected. If the value of RL is 5 kΩ, the resulting voltage is exactly the same as Vshunt. The IC is available in two versions.The INA138 can handle voltages between 2.7 and 36 V, while the INA168 can work up to 60 V. The supply voltage on pin 5 may lie anywhere between these limits, regardless of the voltage on the inputs. This means that even with a supply voltage of only 5 V, you can make measurements with up to 60 V on the inputs! However, in most cases it is simplest to connect pin 5 directly to the voltage on pin 3. Bear in mind that the value of the supply voltage determines the maximum value of the output voltage. Also, don’t forget the internal base-emitter junction voltage of T1 (0.7 V), and the voltage drop across the shunt also has to be subtracted.
Thursday, October 3, 2013
Simple Remote Control Tester

Tuesday, October 1, 2013
Egg Timer Circuit
This is a simple egg timer circuit , which is both simple and functional, shows once again that it is not essential to use a microcontroller for everything these days. The circuit consists of only two ICs from the standard 4000 logic family, a multi-position rotary switch and a few individual components. The combination of a 4040 oscillator/counter and a 4017 decimal counter is certainly not new, but it is an ideal combination for timers that are required to generate long intervals that can be programmed in steps. The circuit can be directly powered from a 9-V battery, without using a voltage regulator. The signalling device is a 12-V buzzer, which generally works quite well even at a much lower voltage. We won’t explain the operation of the two ICs here; if you would like to know more about this, we recommend consulting the device data sheets.
The RC configuration has been selected for the oscillator circuit of the 4060, since the frequencies of standard crystals and resonators would be too high (even 32.768 Hz is much too high), making it impossible to achieve the desired times. With an RC oscillator, it’s also easier to modify the times to suit our purposes. For instance, if the oscillator frequency is reduced by a factor of two, we obtain a range of 1 to 16 minutes in steps of 1 minute. The range is split into two by taking advantage of the fact that the 4017 has an AND gate at its input (with an inverted input).The two ranges overlap by two steps. The oscillator has been dimensioned such that the 23 divider output (pin 14) has a period of 30 seconds, so IC2 receives a clock pulse every 30 seconds. This means that the oscillator frequency must be set to 8.5333 Hz.
The first output of IC2 is active after a reset, so it cannot be used. If S1 is in position I, pin 14 of IC2 is connected to the positive supply line. This input is used as an enable input. Directly after the first pulse from the 4060, the second output of IC2 goes high (which means after exactly half a minute). The sub-sequent outputs become active in turn at intervals of one clock pulse, and thus generate the states for 1 to 4.5 minutes. In the second range (II) of S1, the ‘enable’ pin of IC2 is connected to the 212 divider output of the 4060 (pin 1). This output goes high 4 minutes after the reset (which is why it is labelled ‘240 s’, instead of the period time of 480 s). Since the 4060 is an asynchronous counter, this output goes high a short time after the 23 output goes low. This delay provides the proper condition for an extra clock pulse for the 4017. The outputs of the 4017 will thus count upwards once. This means that the second output will become active after 4 minutes, with the rest of the outputs becoming active after 4.5 to 8 minutes. The desired timing interval is selected using switch S2.
The output of S2 is connected directly to emitter follower T1, which energizes the buzzer when the level on the wiper of the switch is high. At the same time, the counter of IC1 is disabled via diode D1 by forcing the oscillator input high. The buzzer thus remains active until the circuit is switched off. The first counter output of the 4060 is connected to an LED (D2), which indicates that the circuit is active and the battery not yet exhausted. The blinking rate is approximately 0.5 Hz. The current through the LED is set to a modest 1mA, since this current represents the majority of the current drawn by the circuit.
This ranges from 0.5 to 1.5 mA, with the average current consumption being approximately 1mA while the timer is running. The buzzer used in our prototype increases the current to around 13 mA when it is energized, but this naturally depends on the actual type used. In principle, the circuit will work with any supply voltage between 3 and 16 V. However, the actual supply voltage should be taken into account in selecting the buzzer. The value of the supply voltage also has a small effect on the time interval, but in practice, the deviation proved to be less than 5 percent - which is not likely to matter too much to the eggs.
Monday, September 30, 2013
3 Input Video MUX Cable
The circuit diagram shows a low-cost 3-input video MUX cable driver. In this circuit, the amplifier is loaded by the sum of RF and RG of each disabled amplifier. Resistor values have been chosen to keep the total back termination at 75 Ω while maintaining a gain of 1 at the 75-Ω load. The switching time between any two channels is approximately 32 ns when both enable pins are driven. When designing a circuit board for this cable driver, care should be taken to minimize trace lengths at the inverting input. The ground plane should also be pulled away from RF and RG on both sides of the board to minimize stray capacitance. Current consumption of the cable driver is a modest 8mA.
Sunday, September 29, 2013
Two LED Voltage Indicator
Assuming for the moment that R1 is not commented, the output of IC1.A is a square wave with almost 50% duty cycle. The voltage at the junction of R2 and C1 will be a triangular wave (again, almost) with a level determined by the difference in the two threshold voltages of the NAND Schmitt trigger gate IC1.A. IC1.B, IC1.C and IC1.D form inverting and noninverting buffers so that the outputs of IC1.C and IC1.D switch in complementary fashion. With a 50% duty cycle, the red and green LEDs will be driven on for equal periods of time so that both will light at approximately equal brightness resulting in an orange-yellow display. With R1 in circuit, the actual input voltage to IC1.
This is shown in dashed outlines in the circuit diagram. With an 8.2 V zener the dropper resistor should be around 220 ? and R1 has to be reduced to 4.7 k. The LED brightness is determined by R4. As a rule of thumb, R4 = (Vsupply – 2) / 3[k] and remember that the 4093 can only supply a few mA’s of output current. Applications of this little circuit include ‘non critical’ ones such as go/non-go battery testers, simple temperature indicators, water tank level indicators, etc.
Saturday, September 28, 2013
Courtesy Light Extender
This allows Q2 and Q3 to turn on and the courtesy lamp is activated. When the door is closed, the courtesy lamps stay illuminated and the 33µF electrolytic capacitor starts charging through the associated 1MO resistor. As the voltages rises, Q1 turns on slowly, turning off Q2 and Q3 which gradually fades out the courtesy lamp. If a lock signal from the central locking system is received, relay 1 closes and charges the capacitor instantly, so the lamp turns off immediately. Relays were used to interface to the central locking/alarm system as a safety feature, to provide isolation in case something goes wrong.
Friday, September 27, 2013
Long Delay Timer Circuit
Suitable for battery-operated devices, Fixed 35 minutes delay
This timer was designed mainly to switch off a portable radio after some time: in this way, one can fall asleep on the sand or on a hammock, resting assured that the receiver will switch off automatically after some time, saving battery costs.
Circuit operation:
R1 and C1 provide a very long time constant. When P2 is momentarily closed, C1 discharges and the near zero voltage at its positive lead is applied to the high impedance inputs of the four gates of IC1 wired in parallel. The four paralleled gate outputs of the IC go therefore to the high state and the battery voltage is available at Q1 Emitter. When P2 is released, C1 starts charging slowly through R1 and when the voltage at its positive lead has reached about half the battery voltage, the IC gate outputs fall to zero, stopping Q1.
This transistor can directly drive a portable radio receiver or different devices drawing a current up to about 250mA. Connecting a Relay across the Emitter of Q1 and negative ground, devices requiring much higher voltage and current operation can be driven through its contacts. Pushing on P2 for 1 to 5 seconds, the circuit starts and then will switch off after about 35 minutes. This time delay can be varied by changing R1 and/or C1 values. P1 will stop the timer if required.
LED D1 is optional and can be useful to signal relay operation when the load is placed far from the timer.
Circuit diagram:
Long Delay Timer Circuit Diagram
Parts:
R1_________10M 1/4W Resistor
R2_________4K7 1/4W Resistor
R3_________1K 1/4W Resistor (Optional, see Text)
C1_________220µF 25V Electrolytic capacitor
D1_________LED any type and color (Optional, see Text)
D2_________1N4148 75V 150mA Diode (Optional, see Text)
IC1_________4011 Quad 2 Input NAND Gate CMos IC (See Notes)
Q1_________BC337 45V 800mA NPN Transistor
P1,P2______SPST Pushbuttons
RL1________Relay with SPDT 2A @ 230V switch (Optional, see Text)
Coil Voltage 12V - Coil resistance 200-300 Ohm
Notes:
- A 4011 Quad 2 Input NAND Gate was used for IC1, but many other CMos gates or inverter arrays can be used in its place, e.g. 4001, 4002, 4025, 4012, 4023, 4049, 4069. With these devices, all inputs must be tied together and also all outputs, as shown in the Circuit diagram.
- The operating voltage of this circuit should lie in the 6 - 12V range.
Source: www.RedCircuits.com
Thursday, September 26, 2013
2012 Hyundai Genesis Owners Manual
maybe you will need this owner manual so we provides post about this vehicle. beware before you download please to make sure you know this pdf is not on our hosted.
readour privacy first before you download this 2012 Hyundai Genesis Owners Manual
Wednesday, September 25, 2013
Battery powered Night Lamp Circuit
Ultra-low current drawing 1.5V battery supply
This circuit is usable as a Night Lamp when a wall mains socket is not available to plug-in an ever running small neon lamp device. In order to ensure minimum battery consumption, one 1.5V cell is used, and a simple voltage doubler drives a pulsating ultra-bright LED: current drawing is less than 500µA.
An optional Photo resistor will switch-off the circuit in daylight or when room lamps illuminate, allowing further current economy.
This device will run for about 3 months continuously on an ordinary AA sized cell or for around 6 months on an alkaline type cell but, adding the Photo resistor circuitry, running time will be doubled or, very likely, triplicated.
Circuit diagram :
 Battery-powered Night Lamp Circuit diagram
Battery-powered Night Lamp Circuit diagram
Parts:
R1,R2___________1M 1/4W Resistors
R3_____________47K 1/4W Resistor (optional: see Notes)
R4____________Photo resistor (any type, optional: see Notes)
C1____________100nF 63V Polyester Capacitor
C2____________220µF 25V Electrolytic Capacitor
D1______________LED Red 10mm. Ultra-bright (see Notes)
D2___________1N5819 40V 1A Schottky-barrier Diode (see Notes)
IC1____________7555 or TS555CN CMos Timer IC
B1_____________1.5V Battery (AA or AAA cell etc.)
Circuit operation:
IC1 generates a square wave at about 4Hz frequency. C2 & D2 form a voltage doubler, necessary to raise the battery voltage to a peak value able to drive the LED.
Notes:
- IC1 must be a CMos type: only these devices can safely operate at 1.5V supply or less.
- If you are not needing Photo resistor operation, omit R3 & R4 and connect pin 4 of IC1 to positive supply.
- Ordinary LEDs can be used, but light intensity will be poor.
- An ordinary 1N4148 type diode can be used instead of the 1N5819 Schottky-barrier type diode, but LED intensity will be reduced due to the higher voltage drop.
- Any Schottky-barrier type diode can be used in place of the 1N5819, e.g. the BAT46, rated @ 100V 150mA.
Source : www.redcircuits.com
Tuesday, September 24, 2013
Processor Fan Control Circuit
Fans in PCs can be objectionably loud. In many cases, the amount of noise produced by the fan can be considerably reduced by lowering its speed. Although this will decrease the amount of cooling, this need not be a problem as long as you don’t go overboard with slowing down the fan. Particularly with older-model processors, which consume quite a bit less power than the latest models, this trick can be used without any problems. This circuit is anyhow intended to be used with relatively old PCs, since more recent models generally have a fan control circuit already integrated into the motherboard. These controllers ensure that the amount of cooling is increased if the processor becomes too warm and decreased if the processor temperature is relatively low.
Circuit diagram:
Processor Fan Control Circuit Diagram:
The circuit described here consists of only a handful of components, which you will probably already have in a drawer some-where. Transistors T1 and T2 are driven into conduction by the base current flowing to the fan via P1 and D1. There will always be a current flowing through R1, and it will be approximately 120 times as large as the current through R2. R3 has been added to prevent the base current of T2 from becoming too large when P2 is set to its minimum resistance. D1 ensures that even at this extreme setting, the voltage on the base-emitter junction of T3 will still be large enough to allow it to conduct.
Monday, September 23, 2013
Comparator Based Crystal Oscillator

Sunday, September 22, 2013
Portable 9v Headphone Amplifier
Circuit Diagram:

Parts:
P1 = 22K
R1 = 18K
R2 = 68K
R3 = 68K
R4 = 68K
R5 = 18K
R6 = 68K
C1 = 4.7uF-25v
C2 = 4.7uF-25v
C3 = 22pF
C4 = 220uF-25v
C5 = 220uF-25v
C6 = 4.7uF-25v
C7 = 22pF
C8 = 220uF-25v
J1 = 3.5mm Stereo Jack
B1 = 9V Alkaline Battery
IC1 = NE5532-34
SW1 = SPST Toggle Switch
Sensitivity:
200mV RMS for 15.6mW RMS output
350mV RMS for 50mW RMS output
Maximum undistorted output: 3.6V Peak-to-peak
Frequency response: flat from 40Hz to 20KHz; -2.3dB @ 20Hz
Total harmonic distortion @ 1KHz: <0.025% at all power outputs up to 50mW RMS
Total harmonic distortion @10KHz: <0.02% at all power outputs up to 50mW RMS
Total current drawing @ 9V supply (both channels driven):
Standing current: 8.5mA
Mean current drawing @ 15mW RMS per channel: 12mA
Mean current drawing @ 35mW RMS per channel: 17mA
Saturday, September 21, 2013
Fuse Box BMW 325i 1992 Convertible Power Distribution Diagram
Fuse Box BMW 325i 1992 Convertible Power Distribution Diagram
Fuse Panel Layout Diagram Parts: Service Interval Indicator, Tachometer/Fuel Economy Gauges, Gauges/Indicators;, Brake Warning System, Back Up Lights, On Board Computer, Start, Injection Electronics, Active Check Contro, Cruise Control, Injection Electronics, Radio/Antenna, Speedometer/Indicators, On Board Compute, Front Park/Tail, Horn, Rear Defogge, Injection Electronics, Ignition Key Warning/Seatbelt Warning, Auxiliary Fan, Auto Chraging Flashlight, Ignition Key Warning/Seatbelt WarninActive Check Control, Lights, Interior Lights , Central Locking, Radio/Antenna, On Board Computer, Cigar Lighter, Radio/Antenna, Heated/Air Conditioning, Active Check Control, Front Side Marker, Headlights, High Beam Indicator, Headlight, Auxiliary Fan, Lights, Turn/Hazard Warning, Wiper/Washer, Stop Lights, Active Check Control, Antilock Braking System;, Cruise Control, Map Reading Light, Headlights, Heated Seats, Power Windows, Auxiliary Fan, Auxiliary Fan, Interior Light, Power Mirrors, Injection Electronics, Interior Lights, Radio/Antenna, Trunk Light, Active Check Control, Service Interval Indicator, On Board Computer, Tachometer/Fuel Economy Gauge, Electro Mechanical Convertible Top.
Friday, September 20, 2013
1995 Ford Ranger Wiring Diagram
 |
| 1995 Ford Ranger Wiring Diagram |
Thursday, September 12, 2013
Testing A FT245RL Chip with Software

Wednesday, September 11, 2013
KLR250 Chain Adjustment
 To the left is a diagram that shows the chain and sprockets. The part in the middle is the swingarm, which is what the rear wheel is attached to. On the front part of the swingarm there is a plastic chain guard that is held on with one bolt. That bolt is where youll check for slack in the chain which will tell you whether it is adjusted properly or not.
To the left is a diagram that shows the chain and sprockets. The part in the middle is the swingarm, which is what the rear wheel is attached to. On the front part of the swingarm there is a plastic chain guard that is held on with one bolt. That bolt is where youll check for slack in the chain which will tell you whether it is adjusted properly or not.Items Needed:
-Ft/lb torque wrench
-New cotter pin
-Basic hand tools
According to the Kawasaki KLR250 owners manual the correct way to check for proper chain slack begins with placing the bike on its side stand without a driver/passenger on the bike. Because the chain can wear unevenly you should try rotating the rear wheel (WARNING: Watch your fingers by the chain!) until you come to the part where the chain slack is tightest. Then to check for proper slack locate the swingarm guard bolt and directly under it pull the chain up toward the swingarm. The space between the chain and the swingarm should be between 0-5mm or 0-0.2" Check the diagram above for more clarity.
 If the chain is adjusted properly then youre all set, though dont forget to clean and lubricate the chain. If not then its time to make some adjustments. Adjusting the chain is a fairly straight forward process. The rear wheel is held to the swingarm by a long axle with a large nut at the end. That nut is secured in place with a cotter pin. Using a pair of pliers remove the cotter pin and loosen the nut until you can just barely move the adjusters on the axle. (see picture) If you take a close look at the adjusters youll see that they have numbers on them. The higher numbers represent a tighter chain, lower numbers represent a looser chain. All you have to do is turn those adjusters until you see that the chain adjustment is correct, being sure that the adjusters on both sides are on the same number in relation to the metal pin they press against. Failure to make sure both adjusters are in the same position will result in the chain derailing.
If the chain is adjusted properly then youre all set, though dont forget to clean and lubricate the chain. If not then its time to make some adjustments. Adjusting the chain is a fairly straight forward process. The rear wheel is held to the swingarm by a long axle with a large nut at the end. That nut is secured in place with a cotter pin. Using a pair of pliers remove the cotter pin and loosen the nut until you can just barely move the adjusters on the axle. (see picture) If you take a close look at the adjusters youll see that they have numbers on them. The higher numbers represent a tighter chain, lower numbers represent a looser chain. All you have to do is turn those adjusters until you see that the chain adjustment is correct, being sure that the adjusters on both sides are on the same number in relation to the metal pin they press against. Failure to make sure both adjusters are in the same position will result in the chain derailing. Once youve gotten the chain adjusted correctly all that is left to finish up this project is to tighten the axle nut to 69 ft/lbs with a torque wrench and insert a new cotter pin. Before installing the new cotter pin its best to check the chain slack one last time and youre good to go! FYI: Kawasaki recommends checking chain slack every 600 miles.
Note: Eagle eye visitors have pointed out that my adjusters are on upside down. This is the way they were when I purchased the bike. When checking my rear bearings I decided to change them back to the stock setup and found that it was much harder to keep the adjusters in place while tightening the axle nut so I changed them back to this configuration. I can only assume that is why the previous owner set them this way. It works for me so...
Tuesday, September 10, 2013
12V to 220V 100W Transistor Inverter Circuit Diagram

Wednesday, September 4, 2013
Radio Controlled Motor Using AF2310
Both circuits receiver and transmitter are based on the AF2310 integrated circuit .For remote control contacts you can use some push buttons or a mini-joystick .Commands are controlled by different sets of electrical contacts that are used to encode a sequence of electrical pulses; the number of pulses depends on which command is being sent.
An electrical circuit that is tuned to a frequency of 27.9 MHz creates a signal that is sent to the antenna when the pulses are active. The antenna converts the electrical energy into radio energy, creating a stream of radio energy bursts, which travel through the air and are picked up by and understood by the radio receiver in the car. The car antenna collects radio energy and transform it back into electrical energy.If the car is turned on then the radio receiver in the car is continuously monitoring the electrical energy from its antenna.
The receiver is a filter which is tuned to amplify any energy around 27.9 MHz and block energy the antenna picks up outside this region. If the Remote Control Transmitter is sending commands then its radio signal will be picked up by the receiver and converted back into the original pulse sequence. Decoding circuitry then determines which commands were sent by measuring the number of received pulses in the sequence. Signals are then sent to the motors to execute the commands.
When operated with strong batteries and in an open area the range will be at least 40 ft. Obstacles will degrade the radio signal’s ability to travel through air and reduce operating range, but will never block it completely. In the car, weak batteries will reduce power to the Motor and degrade the receiver’s ability to filter, amplify, and decode commands from the Transmitter.
When a command is received to turn left or right, a voltage is applied to the Steering Motor Since the Front Wheels are connected to the Steering Bar, the car will turn. To the turn the other direction, the voltage to the motor is reversed.The Driving Motor works the same as the Steering Motor. When a command is received to go forwards a voltage is applied to the Driving Motor; this voltage is reversed to go backwards.
Tuesday, September 3, 2013
Stereo Balance Indicator
Monday, September 2, 2013
Digital Clock Using with PIC16C54
Digital clock Circuit diagram
The common cathode for each display is turned on with transistors connected to the four I/O lines of PORTA . A low output turns on the PNP transistor for the selected display. The PORTB pins activate the LED segments.
The PORTB pins activate the LED segments. The switches are also connected to PORTB I/O pins.
When no buttons are pressed, the circuit will display the current time, starting at 12:00 on reset.
Pressing SW1 will cause seconds to be displayed. The time is set by pressing SW2 to advance minutes, and SW3 to advance hours . The displays used were common cathode and turned on with transistors to avoid trying to sink too much current into the PIC16C5X. 100 W resistors were used in series with the segments to obtain the desired brightness. Different values may be required if different displays are used.
All of the same display segments are linked together (A-A-A-A, B-B-B-B, etc.) and are individually selected by turning on only the desired display.
This simple digital clock project based on the PIC16C54 microcontroller must be powered from a simple 5 volt DC power supply circuit .
This digital clock project based on the PIC16C54 microcontroller ( circuit and software ) was designed by Dan Matthews Microchip Technology Inc . Download Source Code
Sunday, September 1, 2013
PBL3717A Motor Stepper Driver
PBL3717A Motor Stepper Driver Circuit Diagram
When both of these inputs are high the device is disabled. A separate logic input controls the direction of current flow. A monostable, programmed by an external RC network, sets the current decay time. The output current for this project is up to 1A from 10 up to 46 volt motor supply . The logic inputs I0 and I1 set at three different levels the amplitude of the current flowing in the motor winding .
A high level on the "PHASE" logic input sets the direction of that current from output A to output B and a low level from output B to output A. It is recommended that unused inputs are tied to pin 6 (Vss) or pin 4 (GND) as appropriate to avoid noise problem. The current levels can be varied continuously by changing the reference voltage on pin 11. In this bipolar stepper motor driver project , the Vss is the logic power and must be around 5 volt and VS is the motor power and must be between 10 and 46 volts .

















